What is a Crawl Budget?
The crawl budget is the number of web pages the search bots crawl into at once on a particular website. After the search bots have fulfilled their crawl budget on the site, they move on to a different website. Here, you must know that there is no fixed crawl budget for a website, and it changes from time to time. Some days, it might crawl five pages a day, whereas on other days, it might crawl 100 pages a day. The crawl budget depends on your website’s health and the number of pages it has.
How Does Crawling Work?
Every search engine has its own crawl bots. These bots prepare a list of URLs that they need to crawl on your website. Occasionally, it checks in with the robots.txt file to ensure that the site still allows crawling and crawls through each page individually. The crawl bots crawl through the page’s content and search for URLs (internal links) present in the content. Based on this information, they make a list of other pages on the website that they need to crawl later. After the list is prepared, they move on to another website. This is why it is important to add internal links to the content of your web pages.
Apart from internal links, there are several other reasons as well that help a site become a part of the crawl list. For instance, if someone tweets about a URL, there is a high possibility of the page getting crawled. In other cases, if the website owner decides to update the XML sitemap, the new URLs have a high chance of being noticed by the crawl bots. Honestly, there are numerous reasons why search engines may decide to crawl a page, and it is impossible to come up with a list of fixed criteria.
Why is Crawl Budget Important?
We all know that if Google doesn’t crawl through a page, it will not index it. And, if the page is not indexed, it will not be ranked in the search engine results pages. Hence, to ensure that your page ranks on the SERPs, it is important that Google crawls through each and every page. However, website owners don’t have to worry much about website crawling because the search bots are pretty efficient in finding pages and crawling them for indexing. But, there are a few circumstances where you need to be cautious about your crawl budget:
- If you have 10k+ webpages: If your website has a lot of webpages, generally above 10k, chances are the crawl bots may not be able to index each and every page.
- If you have recently added a lot of new pages: When a website adds a lot of web pages at once, it is difficult for the crawl bots to keep track of these developments and rank the pages.
- If your website has too many redirects: Too many unnecessary redirects mean you are wasting your crawl budget, resulting in the bots not indexing a majority of the pages.
How is Crawl Budget Determined?
The crawl budget of a website is determined by the crawl capacity and demand. Let us understand both of them one by one.
1. Crawl Capacity:
The crawl capacity takes into account the health of your website. If the crawl bots undertake too many pages for crawling, your website may slow down. Your site may not be able to handle too many requests and face performance issues. In addition to this, the search engine’s crawling capacity also determines the crawling limits of the site.
Website’s health: If your website responds to the crawl request quickly, the allotted crawl budget may increase. On the other hand, if the site is taking too much time to complete the crawl request and has recurring server issues, the search engines may limit the overall crawl budget. Therefore, to safeguard your website from this problem, make sure to conduct a site audit at regular intervals and pay close attention to the site load speed and server errors.
Search engine’s crawl capacity: Google doesn’t have an unlimited crawling capacity. Hence, if the crawling capacity of the search engine is impacted due to any reason, the crawl budget is also impacted.
2. Crawl Demand:
If the search engines perceive that your website is important, it will definitely allot a larger crawling budget. The crawl demand is determined by the following factors:
-
- Inventory: Google crawls through every web page on your site. However, if you instruct Google not to crawl through a particular page, they will not. This can be done for duplicate pages through robots.txt file or 404/401 HTTP status code.
- Popularity: When a particular page on your website has a good number of backlinks and organic traffic, it is perceived to be popular by Google and is crawled quickly compared to other pages. Here, you need to remember that backlinks for any random website don’t do the work. The backlinks must be from authoritative and credible sites.
- Freshness: Usually, web pages that are constantly updated are crawled by Google more often. So, if your website has not undergone any updates or changes in a long period of time, the chances of getting crawled by Google are very low.
How Do You Check Your Website’s Crawlability?
A website audit tool is a great device to check the crawlability of a site. Along with this, always make it a point to go through the Google Search Console guidelines to make sure you are following all the regulations. Moreover, this will also help you keep track of any algorithm changes that have been made for crawling.
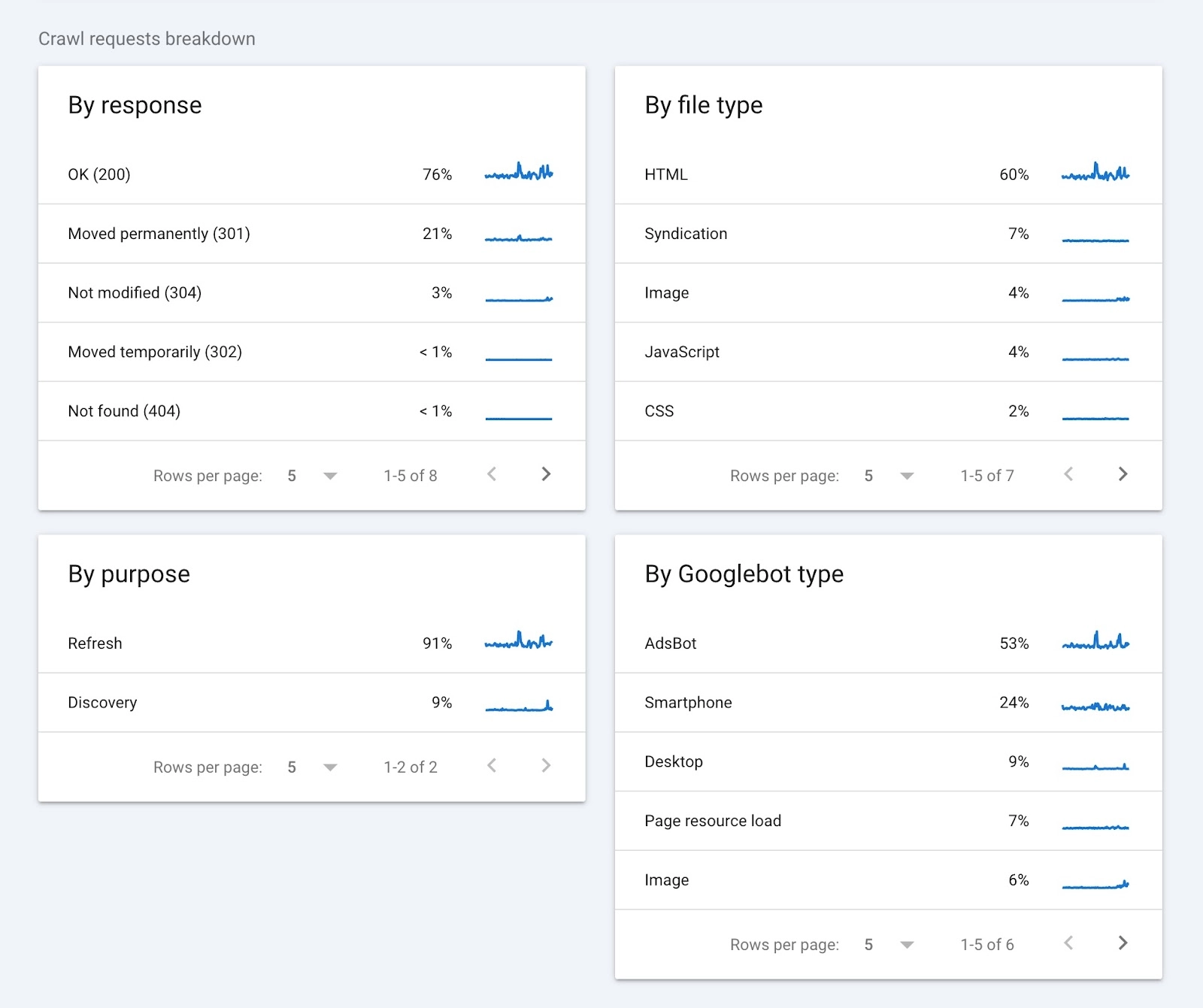
Go to the settings of your Google Search Console account and have a look at the “over-time charts” to get an idea about the number of times Google has made a crawl request on your site in the past 90 days. In addition to this, check the host status to see how easy it is to crawl through the site. Moreover, have a look at the crawl request breakdown for a detailed report.
Best Practices to Improve Crawling and Indexing
Once you have understood the current crawlability status of your website, you must know that there are numerous ways through which you can improve it.
-
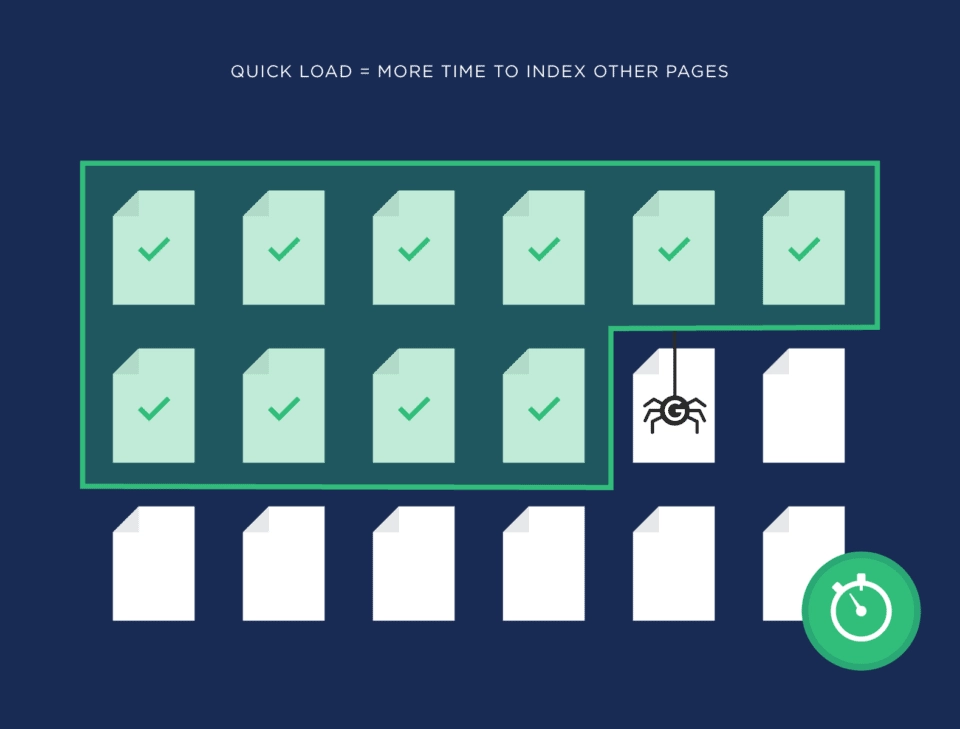
Focus on the Site Speed:
Google loves websites with good site speed. So, if you focus on improving it, you can rest assured that Google crawl bots will crawl through your site and index it more often. When a website has a slow loading speed, it eats up the valuable Google crawling time, which means that fewer pages on your site will be crawled at once. However, when your website has an optimal speed, more pages can be crawled in less time
-
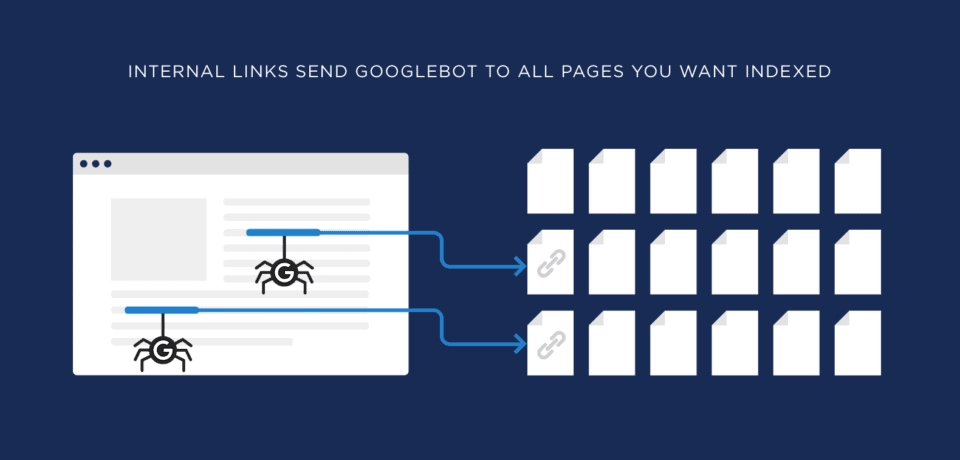
Use Internal Links:
Google appreciates a well-knitted network of internal links. This practice helps the crawl bots make a list of websites they need to crawl next. However, the internal links should not be broken links. Overall, internal linking is the key that helps guide Google to the pages that you want to be indexed on your website.
-
Regular Website Maintenance:
The pages that are crawled must have one of the following return codes: return code 200 for all ok and return code 301 for go here instead. All other return codes are not good for your websites and need immediate attention.
To find the return codes on your site, go to your Google Analytics Account and check the server logs. Now, identify all the common errors and fix the codes.
-
Block Sites Using Robots.txt:
Some of the pages on your website may be underperforming or are under maintenance. In such a case, you can choose to block these sites from Google indexing through robot.txt. By blocking parts of your website, you save your crawl budget and guide Google to index only the pages that you are confident about.
-
Reduce the Number of Redirects:
Although a 301 redirect is good for your website, it is not the best practice. When you use 301 redirects, the new URL may not be immediately crawled. It may just be added to the crawl list of the Google bots for the next time your website is up for indexing. Therefore, you need to avoid a 301 redirect as much as possible.
Conclusion
By now, you know how important it is to optimize your website to make the most out of your crawl budget. Every website has a limited crawl budget, and once you exhaust your budget, Google moves on to a new website for crawling. However, you can make the most out of your crawl budget by continuously analyzing the technical SEO of your website. Search engines need to find your content if you want it to be indexed and ranked. Hence, your website should be free of technical errors, have minimal redirects, and have a great internal linking strategy.