What Are Breadcrumbs?

Breadcrumbs are a navigational feature that shows users the path they have taken to arrive at the current webpage. They appear as a trail at the top of the page, leading from the homepage to the current page. On an e-commerce website, breadcrumbs look like “Home > Electronics > Mobile Phones > Smartphones.” They allow users to backtrack or move easily within categories, which ultimately improves the browsing experience.
For example, if you are on a product page, you might see a breadcrumb trail like this:
Home > Category > Subcategory > Product
Each of these categories in the trail is clickable. So, users can backtrack without using the browser’s “Back” button. This structure helps users and search engines understand your site better.
Types of Breadcrumbs
There are three main types of breadcrumbs used in SEO:
1. Hierarchy-Based Breadcrumbs
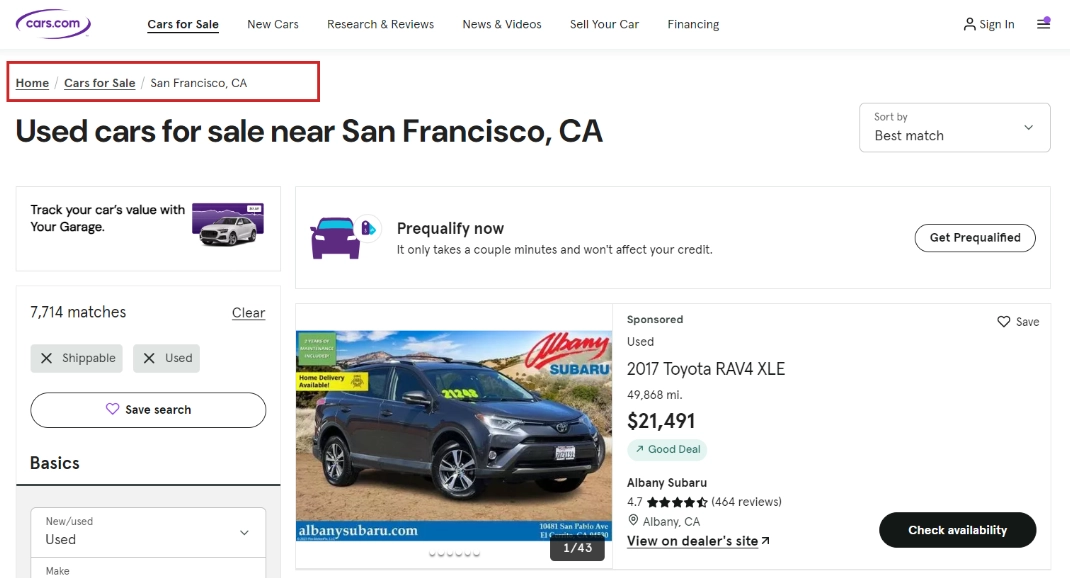
These are the most common and widely used forms of breadcrumbs. They are structured to show where a particular page fits within a website’s overall hierarchy. They allow users to see where they are in the website’s flow.
For example, on an e-commerce site, you may see something like: “Home > Men’s Clothing > T-Shirts > Graphic T-Shirts.” This format is ideal for larger websites where users navigate through different categories. It gives them the flexibility to easily jump back to previous sections with a single click.
When to Use:
Hierarchy-based breadcrumbs are best for websites with multiple levels of content, such as:
- E-commerce stores
- News sites
- Blogs with nested categories
SEO Benefits:
These breadcrumbs reflect your site’s internal structure. This helps search engines understand how your pages are related to each other. This structured data can lead to better crawlability, indexing, and appearance as rich snippets in search engines.
2. Attribute-Based Breadcrumbs
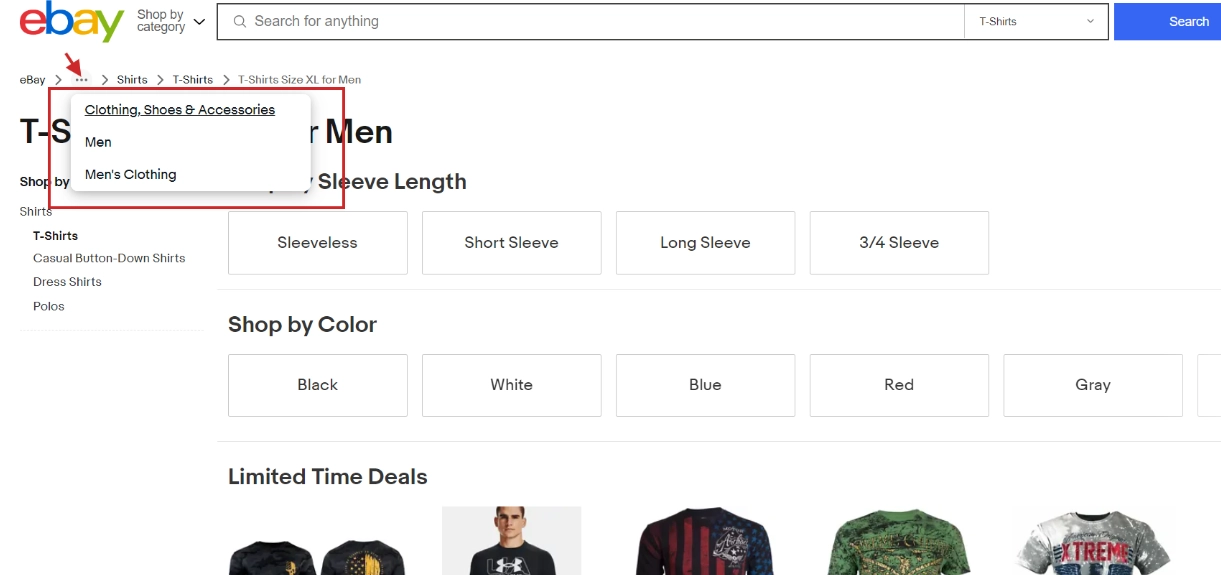
Attribute-based breadcrumbs are more specific to e-commerce websites and catalog-style sites. Instead of showing the user’s position in the site’s hierarchy, they display product attributes the user selects during their journey. This is particularly useful in stores where products have several variations, such as size, color, or category.
For example, if a user is shopping for shoes, the breadcrumbs might read: “Home > Men > Sneakers > Size 10 > Blue.” Each element in this breadcrumb trail represents an attribute the user has filtered. It helps them retrace their steps or adjust their selections as they refine their search.
When to Use:
This type of breadcrumbs is essential for e-commerce sites that offer product filtering. Users can refine their searches by multiple attributes, such as brand, price, color, and size. Attribute-based breadcrumbs make this process much clearer.
SEO Benefit:
Although attribute-based breadcrumbs don’t contribute directly to the overall site hierarchy, they still improve usability. Visitors can engage more with the product catalog. This eventually increases dwell time and reduces bounce rates.
3. Path-Based Breadcrumbs
Path-based breadcrumbs are less common but still useful. Instead of reflecting the structure of the site or product attributes, these breadcrumbs display the exact path the user took to reach the current page. In a way, it’s similar to a browser’s “Back” button but displayed as clickable links on the page itself.
For example, “Home > Search Results > Product Page > Reviews.” These breadcrumbs are particularly helpful when users arrive at a page through a non-traditional route, such as a search function, external links, or a complex series of filters. They offer an easy way for users to backtrack and explore previous pages without relying on their browser’s back button.
When to Use:
Path-based breadcrumbs work best on sites with search functionality or sites where users often follow non-linear paths, like forums, review sites, or complex e-commerce platforms with many filters.
SEO Benefits:
These breadcrumbs don’t provide structural clues to search engines, but they improve user experience by giving visitors a clear route back to previous pages. Smoother navigation leads to longer session times and more page views.
If you have a content-rich site with multiple categories, hierarchy-based breadcrumbs are a must. For e-commerce websites, attribute-based breadcrumbs work best in simplifying product searches. But if your site allows for complex navigational paths, history-based breadcrumbs might be the solution.
Why Are Breadcrumbs Important for SEO?
Breadcrumbs has a pivotal role in SEO. Search engines use breadcrumbs to understand the relationship between different pages on your site. When you add breadcrumbs to your website, you basically provide search engines with a clear path to how content is structured. This can improve crawling and indexing.
Here are some major SEO benefits of using breadcrumbs:
- Improved Site Structure for Google:
Google uses breadcrumbs to understand a website’s architecture. When breadcrumbs are correctly implemented with structured data, they help Google index your content more effectively. The better Google understands your site structure, the better your chances of ranking higher in search results.
- Rich Snippets in Search Engines:
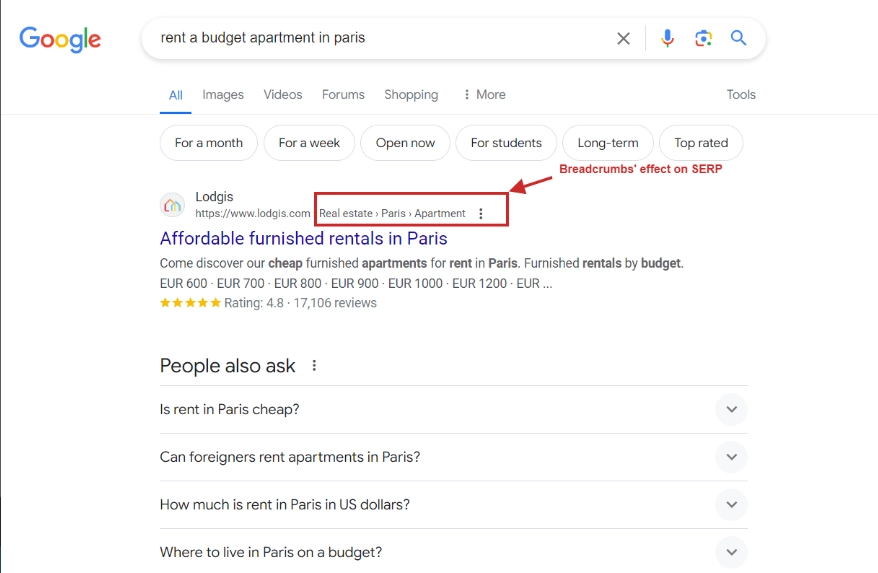
With the right structured data, breadcrumbs can appear in Google’s search results. This makes your website’s listing more attractive. For example, search results might show the full breadcrumb path instead of just a page title. It will provide additional context to searchers and encourage them to click.
- Improved User Experience:
The success of your SEO efforts depends largely on how good your user experience is. Breadcrumbs guide visitors through your website effortlessly. They help them navigate back to previous sections without clicking the back button. This ease of navigation keeps users engaged and improves their overall experience. So, there’s a high chance that the conversion rates will also increase.
- Lower Bounce Rates:
Users land on a page via search engines, bypassing the homepage. If the content they initially find doesn’t meet their expectations, breadcrumbs will provide them with a quick way to navigate to other parts of the site instead of leaving altogether. Offering easy navigation helps reduce bounce rates.
How to Implement Breadcrumbs on Your Website
Implementing breadcrumbs depends largely on your content management system (CMS). However, the type of CMS you use will dictate how you add breadcrumbs to your site.
1. Add Breadcrumbs to Your Site’s Code
The first step in implementing breadcrumbs is adding them to your website’s code. Fortunately, this can be simple, depending on your platform.
For WordPress Users:
There are several plugins available. You can use them to add breadcrumbs without needing to code manually. Plugins include breadcrumbs functionalities that you can easily activate and customize. These plugins offer options to adjust the appearance and behavior of your breadcrumbs, such as their position on the page and the separators used between links.
For Custom Websites:
If you use a custom-coded website, you must manually implement breadcrumbs. Create a breadcrumbs navigation structure in HTML and style it with CSS to fit your website’s design. You will also want to dynamically generate the breadcrumbs trail based on the page’s hierarchy within the site. This requires server-side code like PHP or JavaScript to understand the current page’s position within the structure.
No matter which method you choose, the goal is to provide a clear path back to the homepage from the current page. But breadcrumbs should fit easily within your design without overwhelming the user or taking up too much space.
2. Structured Data Markup for Breadcrumbs
To maximize the SEO benefits of breadcrumbs, you can implement structure data markup. Structured data helps search engines understand the relationship between different pages. It increases your visibility in search results through rich snippets. When you use structured data markup, you are giving search engines exact information about your site’s navigational structure.
Use Schema.org/BreadcrumbList:
This is the schema type recommended for breadcrumbs. The “BreadcrumbList” schema organizes the trail of links into a format that search engines can easily process. Here’s an example of how the markup looks in JSON-LD format:
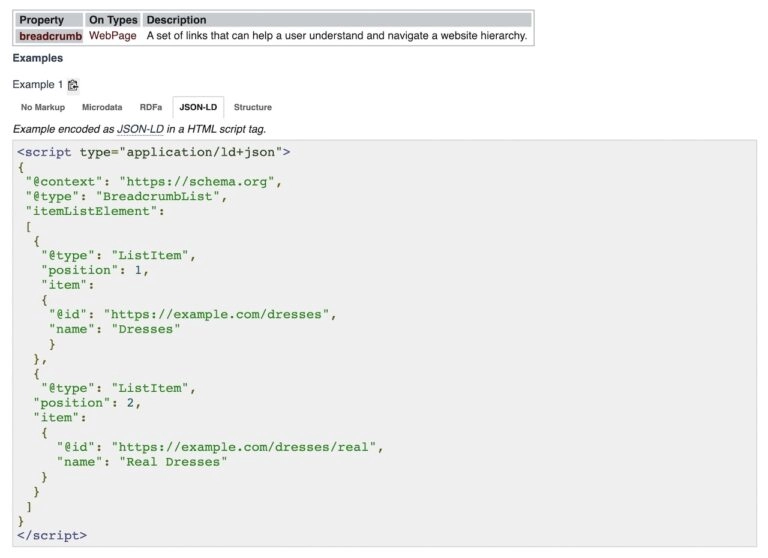
This schema helps Google display your breadcrumbs as rich snippets in search engine results pages. Your site will be more attractive to visitors and improve click-through rates.
Testing Structured Data:
After adding structured data markup, you need to test it using Google’s Rich Results Test or the Schema Markup Validator. These tools can help you check if your breadcrumbs are correctly implemented and if search engines can interpret them as expected.
3. Make Breadcrumbs Clickable
One of the core functions of breadcrumbs is to improve navigation. So, it’s crucial that each element in the breadcrumb trail is clickable, except for the current page. For example, if a user is on a product page, they should be able to click on the category or subcategory to return to those pages.
Clickable breadcrumbs offer users multiple navigation options. They reduce the number of clicks needed to explore related content and categories. This functionality also helps reduce bounce rates. Users can easily find their way around the site without needing to hit the back button repeatedly.
However, it’s best to avoid making the last item in the breadcrumb trail or the current page clickable. Since the user is already on that page, clicking the breadcrumb wouldn’t add any value and might confuse users.
4. Design Breadcrumbs for User Experience
The main reason for implementing breadcrumbs is to make the user experience better. That’s why it’s essential to design breadcrumbs that are clear, intuitive, and subtle.
Use Simple Labels:
Each element in the breadcrumb trail should be labeled in a way that is easy for users to understand. Avoid using overly technical terms or internal jargon that might confuse visitors. Instead, use simple, descriptive labels that indicate the category, subcategory, or page that breadcrumbs represent.
Positioning on the Page:
Breadcrumbs should be placed at the top of the page, just below the navigation bar, where users can easily find them. Place breadcrumbs above the main content. So they could be visible and accessible without detracting from the overall design of the site.
Mobile-Friendly Design:
Your breadcrumb trail should be responsive and work well on smaller screens. Many mobile designs use truncated breadcrumb trails or replace certain elements with a dropdown menu to save space while maintaining usability.
5. Breadcrumbs and SEO Analytics
After implementing breadcrumbs on your website, you need to monitor their performance and impact on SEO. Use tools like Google Analytics and Google Search Console to track how breadcrumbs are affecting major SEO metrics.
Bounce Rate:
If your bounce rate decreases after implementing breadcrumbs, it’s a good sign. That means users are finding it easier to navigate your site and are exploring more pages instead of leaving immediately.
Page Views:
Breadcrumbs can increase the number of pages a user views during a session. This is particularly applicable to e-commerce sites or blogs where users can easily navigate between product categories or related posts.
Average Session Duration:
If breadcrumbs are effective, you may notice that users are spending more time on your site as they navigate between different sections.
Click-Through Rates:
Check how breadcrumbs appear in SERPs and whether they are improving your site’s CTR. Rich snippets that include breadcrumbs can make your site’s listing stand out, leading to higher engagement.
6. Test Breadcrumbs Across Devices
Once your breadcrumbs are live, test them across different devices and browsers. Since users access websites through different devices, consistent functionality and design should be prioritized.
Cross-browser Compatibility:
Check if your breadcrumbs function correctly on all major browsers. They should perform well in Chrome, Firefox, Safari, and Edge.
Mobile Optimization:
Breadcrumbs should resize or reformat appropriately for smaller screens without becoming too small to read or difficult to interact with. Some sites opt for a shorter breadcrumb trail on mobile devices. They collapse intermediate links into a dropdown to save space.
7. Adjust Breadcrumbs Based on Feedback
After analyzing the performance of your breadcrumbs, you may need to make adjustments. For example, if users are not engaging with certain breadcrumb links, you might have to simplify the structure or change the placement. Regularly review user feedback, session recordings, and heatmaps. It can give you better information on how your visitors interact with breadcrumbs.
Conclusion
Including breadcrumbs in your SEO strategy helps improve user navigation. It also helps search engines crawl your website better. It basically provides users with a clear path to navigate on your website. This improves the overall user experience and reduces bounce rates. Implement breadcrumbs correctly with structured data, and you could even boost your search engine rankings.