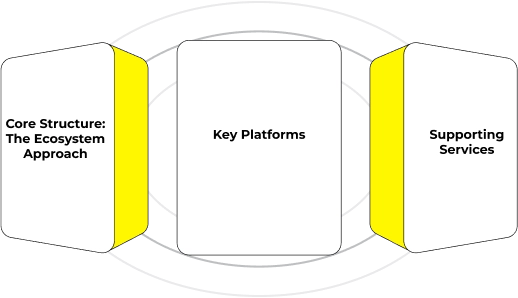
Alibaba Business Analysis: A Deep Dive into China’s E-Commerce Giant

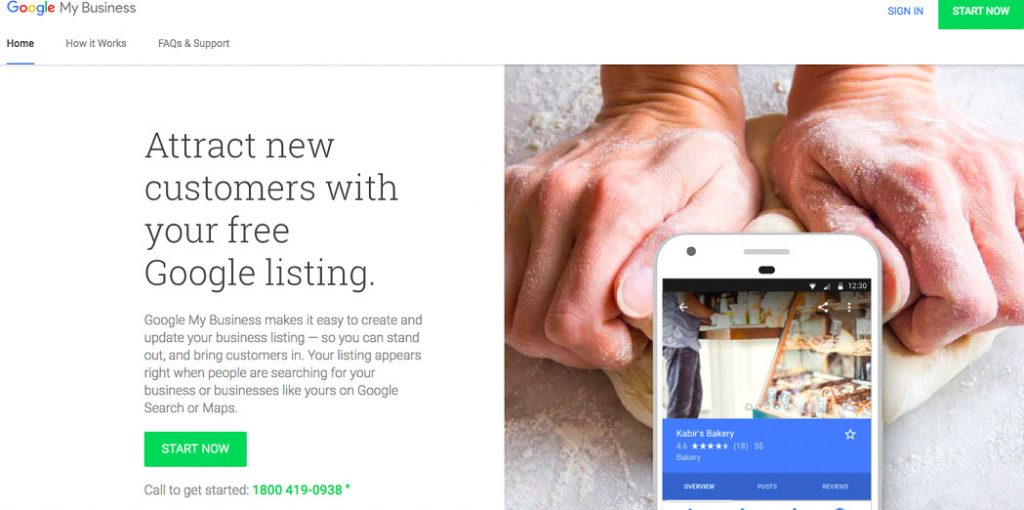
Alibaba is one of the world’s leading e-commerce giants, outperforming the likes of Walmart. Learn more about its unique business approach and market-dominating strategies in this in-depth guide exploring the Alibaba business model.